CONCEPT OF OOP
CONCEPT OF OOP
IMPORTANT QUETIONS FOR EXAM (GTU,CVM,SP)
OOPs Concepts💆:
- Class
- Objects
- Data Abstraction
- Encapsulation
- Inheritance
- Polymorphism
- Dynamic Binding
- Message Passing
1. Class:
A class is a user-defined data type. It consists of data members and member functions, which can be accessed and used by creating an instance of that class. It represents the set of properties or methods that are common to all objects of one type. A class is like a blueprint for an object.
For Example: Consider the Class of Cars. There may be many cars with different names and brands but all of them will share some common properties like all of them will have 4 wheels, Speed Limit, Mileage range, etc. So here, Car is the class, and wheels, speed limits, mileage are their properties.
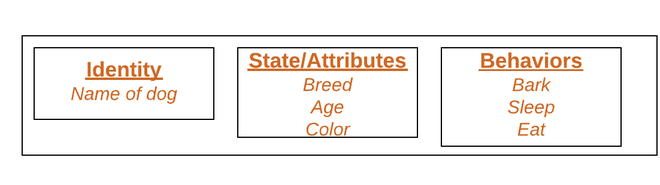
2. Object:
It is a basic unit of Object-Oriented Programming and represents the real-life entities. An Object is an instance of a Class. When a class is defined, no memory is allocated but when it is instantiated (i.e. an object is created) memory is allocated. An object has an identity, state, and behavior. Each object contains data and code to manipulate the data. Objects can interact without having to know details of each other’s data or code, it is sufficient to know the type of message accepted and type of response returned by the objects.
For example “Dog” is a real-life Object, which has some characteristics like color, Breed, Bark, Sleep, and Eats.
3. Data Abstraction:
Data abstraction is one of the most essential and important features of object-oriented programming. Data abstraction refers to providing only essential information about the data to the outside world, hiding the background details or implementation. Consider a real-life example of a man driving a car. The man only knows that pressing the accelerators will increase the speed of the car or that applying brakes will stop the car, but he does not know how on pressing the accelerator the speed is increasing, he does not know about the inner mechanism of the car or the implementation of the accelerator, brakes, etc in the car. This is what abstraction is.
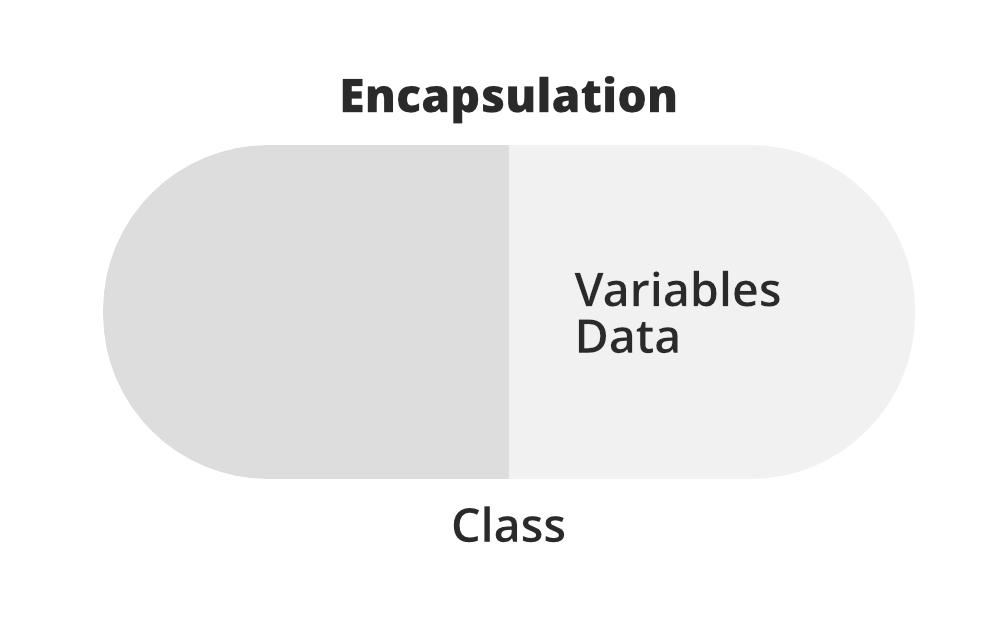
4. Encapsulation: 😕
Encapsulation is defined as the wrapping up of data under a single unit. It is the mechanism that binds together code and the data it manipulates. In Encapsulation, the variables or data of a class are hidden from any other class and can be accessed only through any member function of the class in which they are declared. As in encapsulation, the data in a class is hidden from other classes, so it is also known as data-hiding.
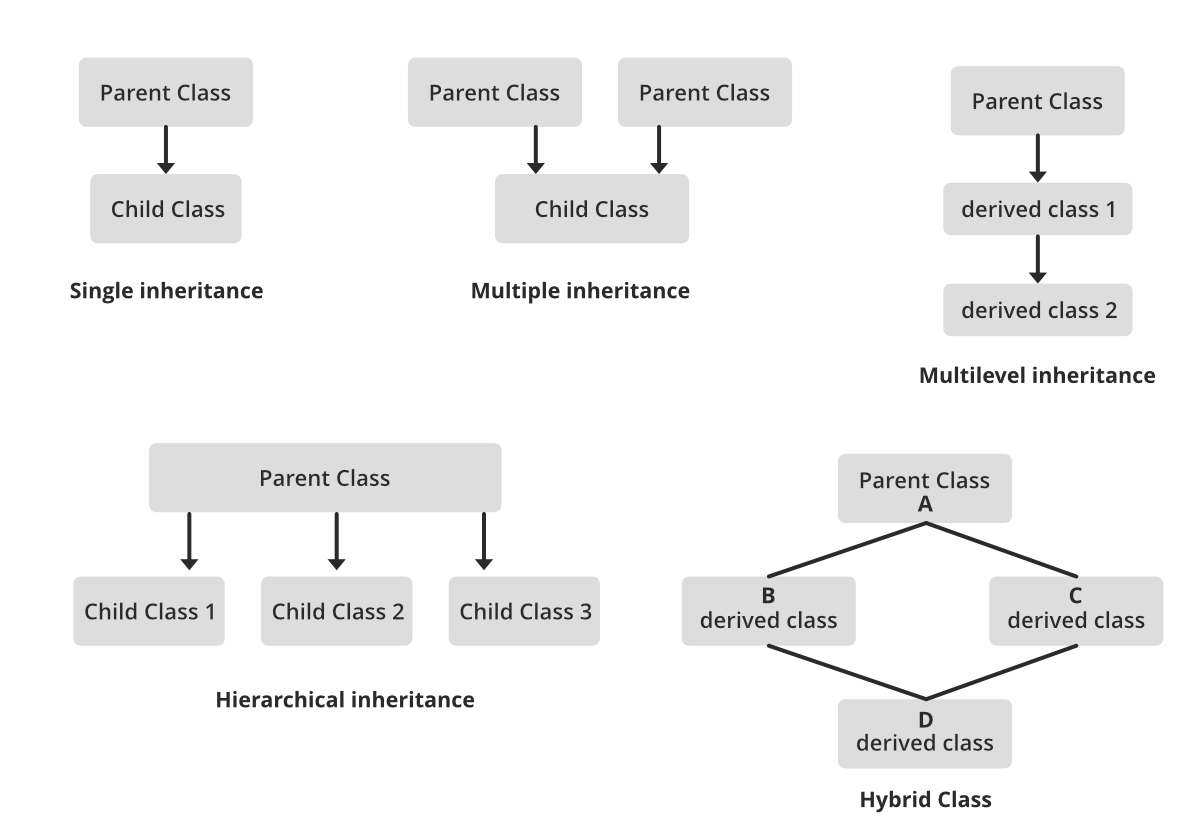
5. Inheritance:
Inheritance is an important pillar of OOP(Object-Oriented Programming). The capability of a class to derive properties and characteristics from another class is called Inheritance. When we write a class, we inherit properties from other classes. So when we create a class, we do not need to write all the properties and functions again and again, as these can be inherited from another class that possesses it. Inheritance allows the user to reuse the code whenever possible and reduce its redundancy.
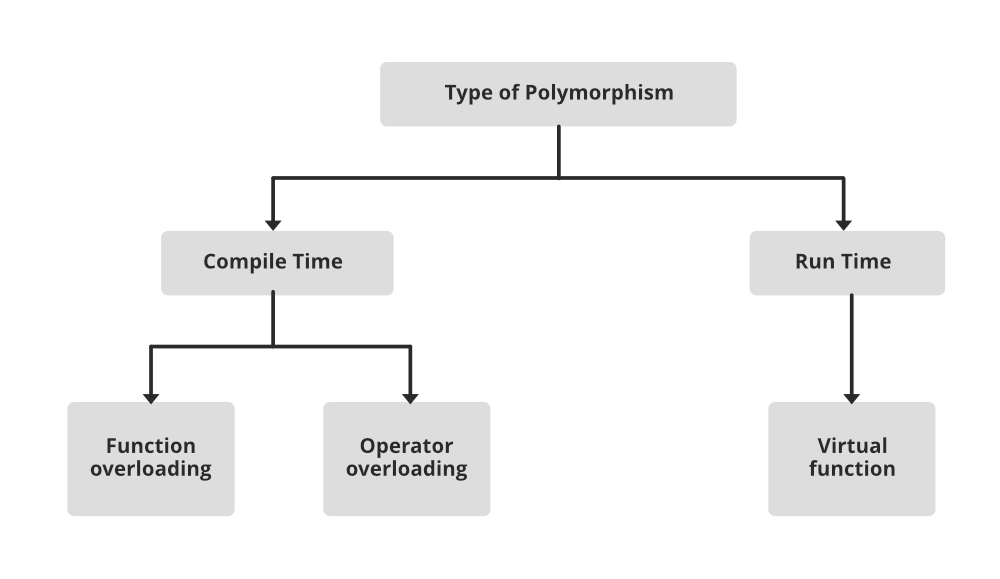
6. Polymorphism:
The word polymorphism means having many forms. In simple words, we can define polymorphism as the ability of a message to be displayed in more than one form. For example, A person at the same time can have different characteristics. A man at the same time is a father, a husband, and an employee. So the same person possesses different behavior in different situations. This is called polymorphism.
7. Dynamic Binding:
In dynamic binding, the code to be executed in response to the function call is decided at runtime. Dynamic binding means that the code associated with a given procedure call is not known until the time of the call at run time. Dynamic Method Binding One of the main advantages of inheritance is that some derived class D has all the members of its base class B. Once D is not hiding any of the public members of B, then an object of D can represent B in any context where a B could be used. This feature is known as subtype polymorphism.
8. Message Passing:
It is a form of communication used in object-oriented programming as well as parallel programming. Objects communicate with one another by sending and receiving information from each other. A message for an object is a request for execution of a procedure and therefore will invoke a function in the receiving object that generates the desired results. Message passing involves specifying the name of the object, the name of the function, and the information to be sent.
BENEFITS AND APPLICANTS OF OOP👤
List out the benefits of OOP.
We can eliminate redundant code through inheritance.
Saving development time and cost by using the existing module.
Build a secure program by data hiding.
It is easy to partition the work into a project based on an object.
Data centered design approach captures more details of a programming model.
It can be easily upgraded from a small to a large system.
It is easy to map objects in the problem domain to those in the program.
Through message passing interface between objects makes simpler description with an external system.
Software complexity can be easily managed.
List out Applications of OOP.
Applications of OOP technology have gained importance in almost all areas of computing including real-time
business systems. Some of the examples are as follows:
1. Real-time systems
2. Simulation and modeling
3. Object-oriented database
4. Artificial intelligence and expert systems
5. Neural networks and parallel programming
6. Decision support and office automation
7. CIM/CAM/CAD systems.
8. Distributed/Parallel/Heterogeneous computing
9. Data warehouse and Data mining/Web mining
OOP Vs POP👭
| OOP | POP |
|---|---|
| Object oriented. | Structure oriented. |
| The program is divided into objects. | The program is divided into functions. |
| Bottom-up approach. | Top-down approach. |
| Inheritance property is used. | Inheritance is not allowed. |
| It uses an access specifier. | It doesn’t use an access specifier. |
| Encapsulation is used to hide the data. | No data hiding. |
| Concept of virtual function. | No virtual function. |
| C++, Java. | C, Pascal. |

What about other chapters
ReplyDelete